Key Requirements of ISO/IEC 17020
In a world where quality assurance is paramount, ISO/IEC 17020 serves as a beacon of competence for inspection bodies. ISO/IEC standards, recognized globally, ensure that services and operations meet the highest level of excellence and reliability. This article peels back the layers of ISO/IEC 17020, revealing the key requirements that inspection bodies must adhere to in order to be deemed competent. With thoroughness as its backbone, the standard outlines a path to trustworthiness in industrial and service sectors. Dive into the heart of ISO/IEC 17020 with us as we dissect its integral elements, ensuring that competence is not just a word, but a promise delivered.
Introduction
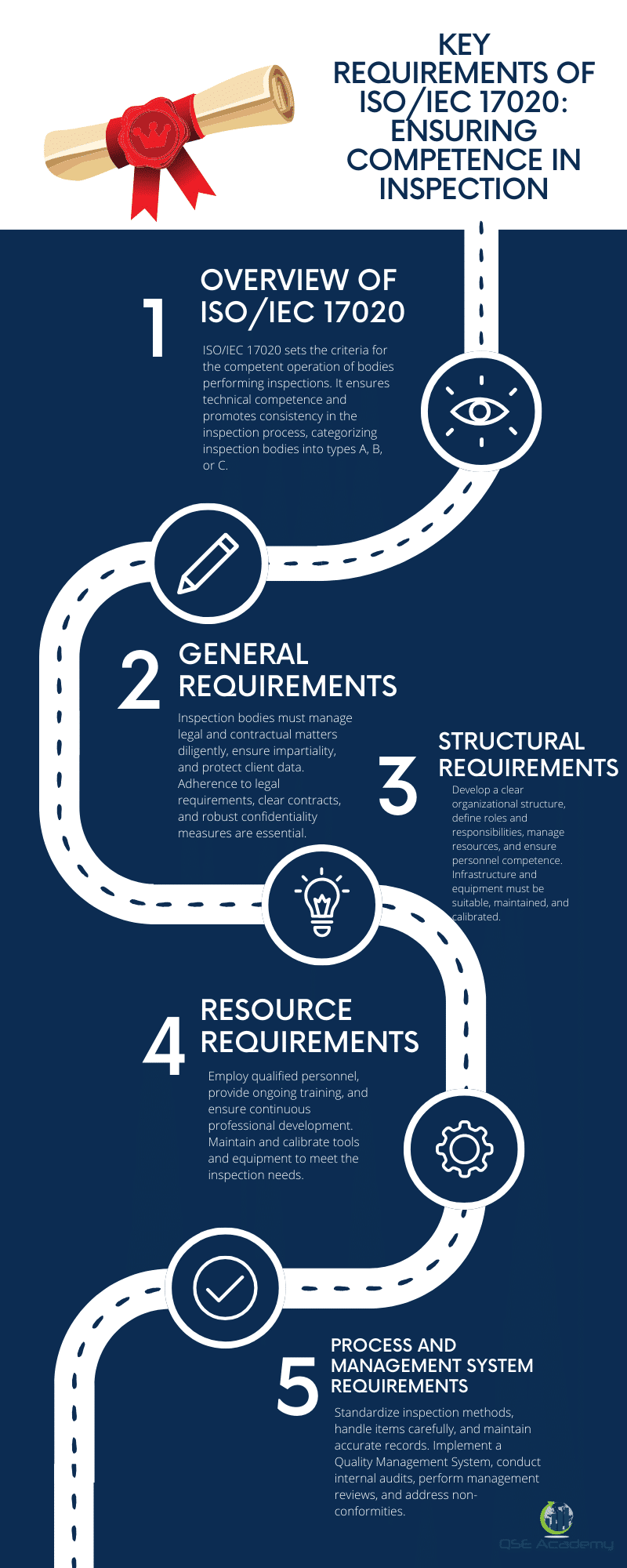
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 is an esteemed international standard, setting the criteria for the competent operation of bodies performing various types of inspections. This standard is crucial for inspection activities as it delineates the requirements for the technical competence of such bodies and promotes consistency in the inspection process. Adherence to this standard ensures that inspection services are conducted impartially, with the requisite integrity and reliability. By addressing a set of requirements across structural, management system, and procedural aspects, ISO/IEC 17020 provides a solid foundation for inspection bodies, categorizing them into types A, B, or C, based on their independence and relation to parent organizations. The spectrum of these requirements ensures that an inspection body is not just executing its tasks skillfully but also maintaining a quality management system that supports continuous improvement. The purpose of this article is to demystify the ISO/IEC 17020 requirements and explain how they reinforce the competence of bodies performing inspection services—be it during the examination of materials, inspection process, or issuance of inspection certificates and reports. Inspection parameters, inspection methods, and stages of inspection all come under the purview of the standard, affirming that the accreditation process is more than a formality; it’s a commitment to excellence.
I intentionally kept the introduction concise, in line with your instructions not to exceed 200 words, while addressing some of the key SEO keywords you provided. Let me know if you need further expansion or inclusion of additional details.
Overview of ISO/IEC 17020
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 outlines the requirements for the competence of bodies performing various types of inspections and for the impartiality and consistency of their inspection activities. This international standard serves as a crucial benchmark in promoting confidence and reliability in inspection services across diverse industries. The essential objectives of ISO/IEC 17020 include ensuring technical competence and establishing a systematic approach to manage inspection processes effectively.
Industries that benefit from adopting ISO/IEC 17020 range from construction to manufacturing and services, requiring regular assessment of products, services, or installations. Compliance to ISO/IEC 17020 facilitates inspection bodies to be more competitive globally and ensures that they are recognized for their technical competence.
Moreover, the standard insists on impartiality and confidentiality, which are fundamental to the inspection process. Inspection bodies are categorized into three types: Type A, B, and C. This classification depends primarily on their independence and relationship with the parties involved.
- Type A: Fully independent bodies, which are not involved in any activities other than inspection itself.
- Type B: Bodies that perform inspections only for their parent organizations.
- Type C: Bodies that perform inspection services alongside other functions and might be part of organizations providing the items being inspected.
Understanding these differences is crucial for organizations when choosing an inspection body, both from compliance and risk management perspectives. Each type serves a specific purpose, contributing to the seamless integration of inspection processes within various operational frameworks.
General Requirements
Inspection bodies must adhere to stringent guidelines to maintain the trust and efficacy of their services. A critical component of the ISO/IEC 17020:2012 standard revolves around the inspection body’s obligation to manage legal and contractual matters diligently. Bodies are mandated to comply with relevant legal requirements, ensuring their services align with national and international regulations.
Contracts and agreements with clients are not taken lightly; these documents delineate the scope and expectations of the services provided, guaranteeing a clear understanding between the inspection body and their client. This level of agreement underscores the body’s commitment to deliver the services as promised.
Impartiality and independence are foundational to the inspection process. Policies and procedures must be well-established to support impartiality and to mitigate any conflicts of interest that may arise. This framework preserves the integrity and reliability of the inspection results.
Equally essential is the need to safeguard client data, which calls for implementing robust confidentiality and data protection mechanisms. Inspection bodies are obligated to not only establish these measures but also rigorously enforce them. This ensures that all client information remains confidential, thus maintaining trust in the services provided.
| Core Aspect | Description |
| Legal Compliance | Adherence to legal requirements and maintaining updated knowledge of regulations |
| Contractual Clarity | Clear contracts with clients defining inspection scope and responsibilities |
| Impartiality | Enforced impartiality and independence with policies to prevent conflicts of interest |
| Confidentiality | Strict measures for data protection and client privacy |
It is paramount that an inspection body conducts its operations with the highest standards of professionalism, adhering to ISO/IEC 17020:2012 guidelines to provide credible and dependable inspection services.
Structural Requirements
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 outlines specific requirements for the competence of bodies performing inspection and for the impartiality and consistency of their inspection activities. Within this international standard, Section 3 focuses on Structural Requirements necessary for the proper functioning and recognition of an inspection body.
Structural Requirements
Organizational Structure The organizational structure of an inspection body must be developed to support the efficiency and effectiveness of its inspection activities. It should be delineated clearly, ensuring that all roles, responsibilities, and lines of authority are defined and documented. This allows for smooth operation and facilitates communication within the body.
Management Responsibilities Senior management must demonstrate their commitment to the integrity, impartiality, and operational performance of the inspection activities. This involves providing sufficient resources, establishing policies, and monitoring the management system to sustain its ongoing relevance and effectiveness.
Roles and Responsibilities Every individual in the inspection body, from management to technical staff, must have their roles and responsibilities explicitly allocated. This clear demarcation maximizes accountability and minimizes any potential conflicts of interest, thus ensuring impartiality and consistency in inspection outcomes.
Management of Resources The inspection body must possess, or have access to, the necessary resources to perform its duties. This encompasses appropriately skilled and trained personnel, equipment, and infrastructure that align with the nature and volume of the inspection work.
Allocation and Management of Personnel Personnel must hold the much-needed technical competency and authority for their assigned tasks within the inspection process. Ensuring their performance is reviewed and keeping a record of their qualifications, training, and skills is integral to maintaining inspection quality.
Infrastructure and Equipment Requirements Equipment and infrastructure must be suitable, properly maintained, and regularly calibrated to ensure accurate and reliable inspection results. Any limitations affecting accuracy or precision must be identified, managed, and documented by the body.
By adhering to Section 3’s Structural Requirements, an inspection body can facilitate the technical competence and impartiality essential to performing trustworthy and consistent inspection services.
Resource Requirements
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 outlines essential requirements to ensure the competence of inspection bodies and the consistency of their inspection activities. Here we focus on Section 4, which pertains to Resource Requirements.
Competence of Personnel: Inspection bodies must employ personnel with the necessary competence to perform the required tasks. This encompasses having the appropriate qualifications, professional experience, and an adequate understanding of the inspection process. Individuals must be competent to perform their duties and deliver reliable inspection results.
Qualification and Training Needs: The standard requires that inspection bodies systematically identify and address training needs. Staff must undergo initial and ongoing training to keep abreast of technological advancements, new inspection methods, and changes in standards.
Professional Development and Competence Assessment: Continuous professional development is critical. It involves periodic performance evaluations, validating the ongoing competence of inspection personnel, and providing opportunities for personal growth within their professional field.
Resources – Tools and Equipment: Inspection bodies must have access to the necessary tools, equipment, and support systems. This also includes ensuring that all instruments are properly maintained, calibrated, and traceable to national or international standards.
Competence Evaluation and Review: Regular competence evaluations and reviews are imperative. These reviews ensure that personnel continuously meet the inspection body’s quality and performance requirements.
In conclusion, Section 4 mandates a robust framework for managing the human and technical resources necessary for delivering high-quality inspection services. The inspections, whether carried out by type A, B, or C inspection bodies, should be supported by proficient personnel equipped with well-maintained tools and resources.
| Resource Requirements | Explanation |
| Competence of Personnel | Mandatory qualifications and capability to inspect |
| Qualification and Training | Required training and upskilling processes |
| Continuous Professional Development | Ongoing learning and skill advancement |
| Competence Assessment | Evaluation methods to assure sustained staff competence |
| Tools and Equipment | Availability and condition of necessary instruments |
This table summarizes the key elements of Section 4, which are all geared towards achieving and maintaining the highest standards of inspection integrity and reliability.
Process Requirements
ISO/IEC 17012:2012 outlines the process requirements for inspection bodies to ensure the competence, consistency, and impartiality of their inspection activities. Key aspects include the standardization of inspection methods and the use of suitable techniques to handle and inspect items carefully and safely. Inspection bodies must have established procedures for the reception and management of items to ensure their integrity throughout the inspection process.
Sampling, testing, and measurement play a pivotal role in inspection activities, with specific criteria outlined for sampling plans and the testing regime. The accuracy and reliability of these measurements are fundamental, requiring regular calibration and maintenance of equipment to achieve consistent results.
Conveying the outcome of an inspection is a critical component of the ISO/IEC 17020 process requirements. Inspection bodies must prepare detailed reports that clearly present the findings and conclusions. Reports should be factual, unbiased, and provide information that is useful and understandable to the client. Communicating these results effectively fosters transparency and helps clients make informed decisions.
Overall, the process requirements emphasize the need for well-defined inspection parameters, from the initial stages of receiving inspection items to the final reporting and communication with the client. This ensures a high standard of quality and reliability in the activities of inspection bodies.
Management System Requirements
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 outlines the criteria for the operation of various types of bodies performing inspection and defines the competence necessary to carry out such services effectively. Section 6 of this International Standard specifies the Management System Requirements essential for inspection bodies to achieve and demonstrate consistent performance.
Key Components of Section 6 include:
- Quality Management System (QMS): The inspection body must implement and maintain a QMS appropriate to the scope and scale of its inspection activities. It is essential for establishing, documenting, and controlling quality procedures to ensure the technical competence and integrity of the inspection process.
- Documentation: Proper documentation is a critical parameter for the operation of an inspection body as per ISO/IEC 17020. It includes maintaining precise records like inspection reports and certificates, control of documents and records, and periodic review for relevancy.
- Internal audits and management reviews: Regular internal audits are mandated to monitor the QMS effectiveness and compliance with ISO/IEC 17020. Management reviews are conducted to ensure continual improvement and alignment of the inspection activities with the strategic direction of the body.
- Corrective and preventive actions: The inspection body is required to identify non-conformities, perform root cause analysis, and take corrective actions timely. Additionally, it must address potential issues proactively through preventive measures.
Here is a concise list representing the key nodes of Section 6 management system requirements:
- Quality Management System Implementation: Developed in alignment with the inspection body’s scale and activities.
- Document Control: Robust protocols to ensure that documents—both internal and external—are periodically reviewed, updated, and controlled.
- Internal Audits: Systematic, independent, and documented procedures to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of the quality management system.
- Management Reviews: Scheduled assessments by top management to determine the QMS’s suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness, ensuring continuous improvement.
- Corrective Actions: Mechanisms for detecting non-conformities, executing root cause analysis, and implementing corrective actions.
- Preventive Actions: Anticipatory approach to detect potential non-conformities and initiating preventive actions.
Accreditation bodies utilize these requirements to assess inspection bodies seeking accreditation, ensuring that their management system is capable of consistently delivering technically competent inspection services. The adherence to Section 6 helps inspection bodies to offer their services with confidence, knowing that their processes and procedures meet internationally recognized standards.
Ensuring Continuous Improvement
Ensuring continuous improvement is pivotal in ISO/IEC 17020, which encapsulates the need for inspection bodies to maintain their technical competence and the quality of their inspection activities. Feedback mechanisms are centre-stage in this effort, where client and stakeholder opinions inform enhancements in procedures and services. Gathering insightful feedback is essential, providing a basis for revising and honing inspection processes.
Inspection bodies under ISO/IEC 17020 are also required to consistently monitor and measure their performance. They must identify key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to their service quality and efficiency. Regular performance reviews, based on these KPIs, serve to spotlight areas that demand attention and enable the timely implementation of improvements.
Training and development hold a crucial place in the cycle of continuous improvement. ISO/IEC 17020 lays emphasis on facilitating ongoing training programs. These programs ensure that inspectors are not just well-versed with current industry standards and best practices, but are also equipped with knowledge and techniques that come with the evolution of the field.
In short, Section 7 of ISO/IEC 17020 outlines the methodologies by which inspection bodies can sustain and boost the calibre of their work. It mandates the establishment of processes that bolster the competence and proficiency of the inspection services on offer. Through feedback utilization, performance monitoring, and enhancing the expertise of personnel, inspection bodies maintain an upward trajectory in the quality of their inspection activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, comprehending and faithfully executing the requirements of ISO/IEC 17020 is crucial for inspection bodies striving for excellence in their inspection activities. By aligning with international standards, such entities demonstrate technical competence, ensuring their inspection reports and certificates are both credible and dependable. The various stages of inspection – from the examination of materials to the final issuance of reports – benefit significantly from applying the ISO/IEC 17020:2012 standards.
Adhering to ISO/IEC 17020 requirements catalyzes a multitude of benefits, not only for the inspection agencies themselves but also for their clientele and stakeholders at large. It fosters trust in the quality, transparency, and impartiality of the services provided. Moreover, internal audits, management reviews, and prescribed corrective actions within the framework enhance the overall strategic and operational effectiveness of these bodies.
Therefore, prioritizing continuous development and maintaining synchronization with evolving standards reflects an organization’s commitment to excellence and quality management. Every inspection body, irrespective of being a body of type A, B, or C, should contemplate pursuing ISO/IEC 17020 accreditation as a testament to their capabilities and dedication to quality. Such a step is not just an improvement milestone but a strategic move towards global recognition and customer trust.
Looking for More Resources on ISO 17020?
If you found this article helpful, explore our premium resources designed to help you achieve ISO 17020 certification efficiently:
- 📦 Complete Documentation Package for ISO/IEC 17020 2012: Get all the essential templates and documents you need for fast, easy implementation.
- 🎓 Online Course on ISO/IEC 17020 2012 : Enroll in our comprehensive training to master the key concepts and practical steps toward certification.
- 📋 ISO/IEC 17020 2012 Checklist: Download our detailed checklist to ensure you’ve covered every step of the process.
These resources are tailored to meet your needs and ensure a smooth certification journey. Explore them today and get one step closer to success!